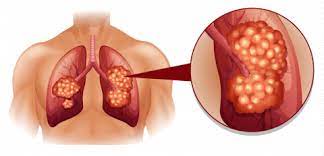
Mesothelioma is cancer of the mesothelium, a membrane that lines the inside of the body's cavities, such as the abdomen or chest. Three out of every four cases of mesothelioma disease begin in the chest cavity. Mesothelioma can also begin in the abdominal cavity and around the heart.
Mesothelioma is an aggressive and deadly form of cancer. Mesothelioma treatments are available, but for many people with mesothelioma, a cure isn't possible.
Research shows approximately 8% to 13% of asbestos workers eventually develop Mesothelioma.
The most Common Symptoms of Mesothelioma are :
- Fever
- Weight Loss
- Blood Clotting Abnormalities
- Shortness of Breath
- Ascites
- Swelling and Pain in the Abdomen
Factors that may increase the risk of Mesothelioma include :
- Personal History of Sbestos Exposure : If you've been directly exposed to asbestos fibers at work or at home, your risk of mesothelioma is greatly increased.
- Living with someone who works with asbestos : People who are exposed to asbestos may carry the fibers home on their skin and clothing. Exposure to these stray fibers over many years can put others in the home at risk of mesothelioma. People who work with high levels of asbestos can reduce the risk of bringing home asbestos fibers by showering and changing clothes before leaving work.
- A Family History of Mesothelioma : If your parent, sibling or child has mesothelioma, you may have an increased risk of this disease.
- Radiation Therapy to the Chest : If you had radiation therapy for cancer in your chest, you might have an increased risk of Mesothelioma.
What causes Mesothelioma ?
The main risk factor for Mesothelioma is working with asbestos. Asbestos is a group of minerals with thin microscopic fibers. Because these fibers are resistant to heat, fire, and chemicals and do not conduct electricity, asbestos has been mined and used widely in the construction, automotive, and other industries.
These tiny fibres can easily get in the lungs, where they get stuck, damaging the lungs over time.
Complications for Mesothelioma :
- Pain caused by pressure on the nerves and spinal cord
- Difficulty Breathing
- Chest Pain
- Accumulation of fluid in the chest (pleural effusion), which can compress the lung nearby and make breathing difficult
- Difficulty Swallowing
Surgery :
- Wide local excision, which removes the cancer along with some of the healthy surrounding tissue
- Pleurectomy and decortication, in which the surgeon removes part of the covering of the lungs, chest lining, and outside surface of the lungs Extrapleural pneumonectomy, which involves removing one whole lung and part of the lining of the chest, the diaphragm, and the lining of the sac around the heart.
Radiotherapy : This type of cancer treatment uses high-energy X-rays and other types of radiation to kill mesothelioma cells or keep them from growing. Radiation may be given externally or internally. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Internal radiation uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into the area near the mesothelioma.
Chemotherapy : This uses drugs to stop the growth of cancerous mesothelioma cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy can be given by mouth, injected into a vein or muscle to enter the bloodstream and reach mesothelioma cells throughout the body, or it can be placed directly into the affected area of the body to mainly affect mesothelioma cells in that area. Sometimes, doctors use more than one chemotherapy drug. This is called combination chemotherapy.