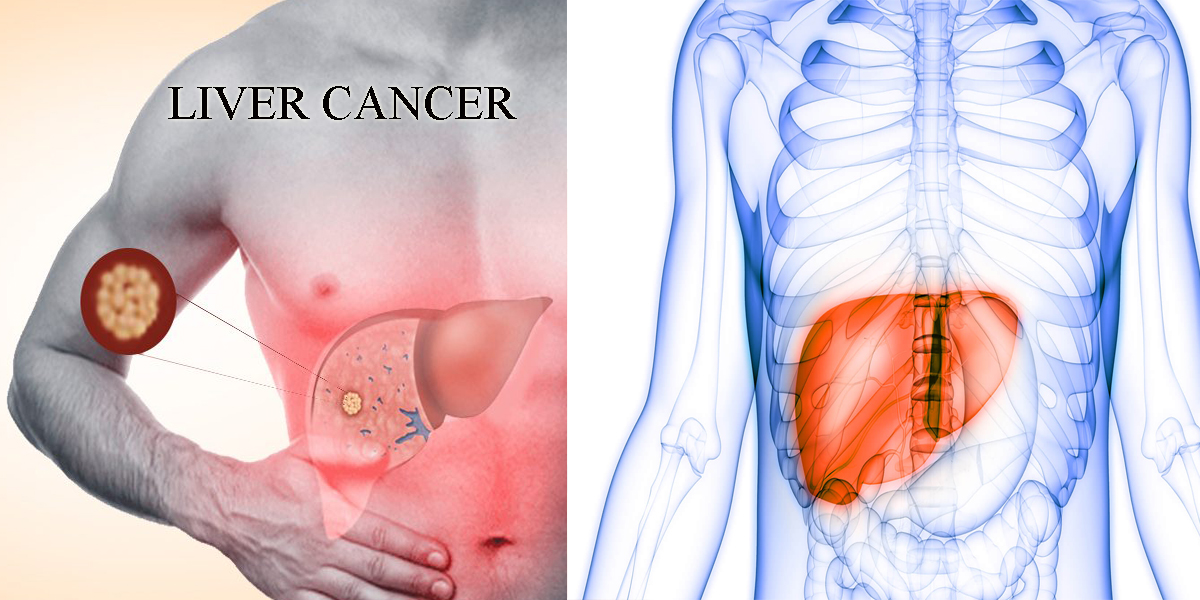
Liver Cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach.
Cancer are spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung or breast — and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than Liver Cancer.
Once Liver Cancer is diagnosed, your doctor will work to determine the extent (stage) of the cancer. Staging tests help determine the size and location of cancer and whether it has spread.
Other types of Liver Cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cancer include :
- Losing Weight without trying
- Loss of Appetite
- White, Chalky Stools
- Upper Abdominal Pain
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Yellow discoloration of your skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- General Weakness and Fatigue
- Abdominal Swelling
Factors that increase the Risk of primary Liver Cancer include :
- Chronic infection with HBV or HCV.
- Cirrhosis.
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Exposure to Aflatoxins
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Diabetes.
- Cirrhosis
Tests and Procedures used to diagnose Liver Cancer include:
- Blood Tests.
- Imaging Tests.
- Removing a sample of liver tissue for testing.
Localized treatment options for Liver Cancer include :
- Placing beads filled with radiation in the liver.
- Injecting chemotherapy drugs into the liver.
- Heating Cancer Cells
- Freezing Cancer Cells.
- Injecting Alcohol into the Tumor