Gastrointestinal Cancers
Generally speaking, Gastrointestinal Cancers are more likely to develop in men, and the risk increases with age. Studies have linked these cancers to cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption and unhealthy diets.
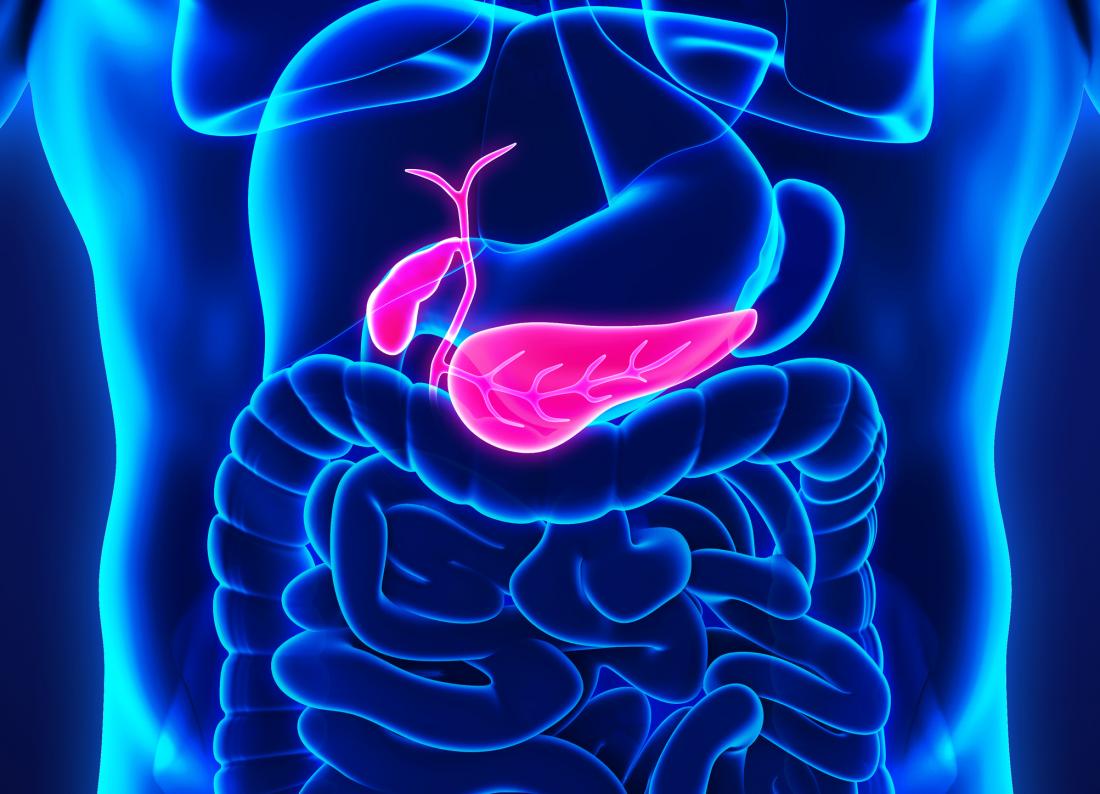
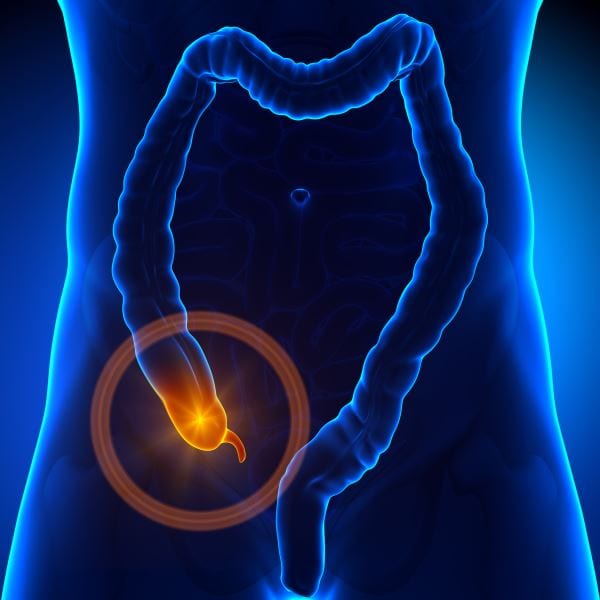
Gastrointestinal Cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) and accessory organs of digestion, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
Treatment of this type of cancer depends on many factors such as type of cancer, stage and other general health factors. The two major treatment options for GI cancers are chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Gastroenterology is the normal function and diseases of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon and rectum, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts and liver
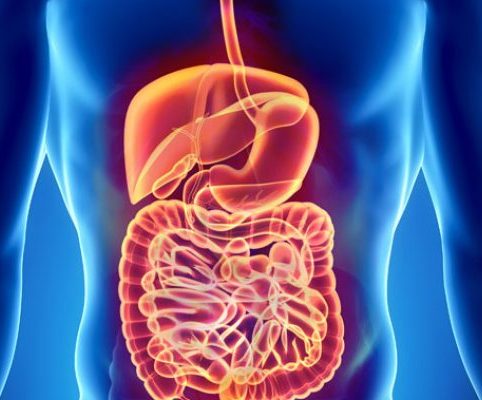
Risk factors for developing Gastrointestinal Cancer :
Gastrointestinal Cancer signs and symptoms may include :