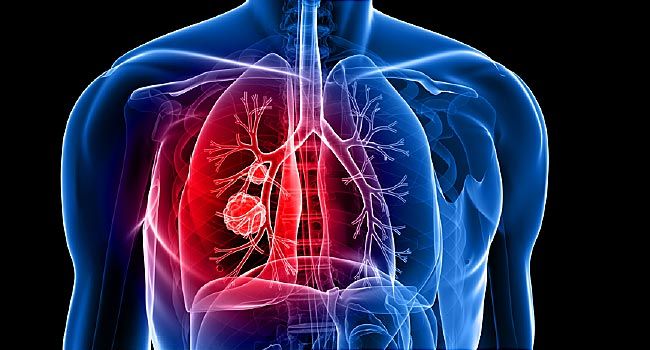
Lung Cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells that line the air passages. It is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women.
The two main types of Lung Cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, depending on how they appear under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer.
What Causes Lung Cancer ?
Smoking causes the majority of Lung Cancers both in smokers and in people exposed to secondhand smoke. But Lung Cancer also occurs in people who never smoked and in those who never had prolonged exposure to secondhand smoke. In these cases, there may be no clear cause of Lung Cancer.
Small cell Lung Cancer : Small cell lung cancer occurs almost exclusively in heavy smokers and is less common than non-small cell lung cancer.
Non-small cell Lung Cancer : Non-small cell lung cancer is an umbrella term for several types of lung cancers. Non-small cell lung cancers include squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma and large cell carcinoma.
Signs and symptoms of Lung Cancer include :
- A new cough that doesn't go away
- Coughing up blood, even a small amount
- Shortness of Breath
- Chest Pain
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss with no known cause.
- Shortness of Breath.
Risk of factors for Lung Cancer include :
- Personal or Family History of Lung Cancer
- Exposure to Secondhand Smoke
- Smoking
- Diet
- Previous Radiation Therapy..
- Exposure to Asbestos and other Carcinogens
- Surgery :
Surgery to remove part or all of a Lung.
- Chemotherapy. :
Chemotherapy Using special medicines to shrink or kill the cancer. The drugs can be pills you take or medicines given in your veins, or sometimes both.
- Radiation Therapy :
Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy beams from sources such as X-rays and protons to kill cancer cells. During radiation therapy, you lie on a table while a machine moves around you, directing radiation to precise points on your body.
- Immunotherapy :
Immunotherapy treatments are generally reserved for people with locally advanced lung cancers and cancers that have spread to other parts of the body
- Targeted Therapy :
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.