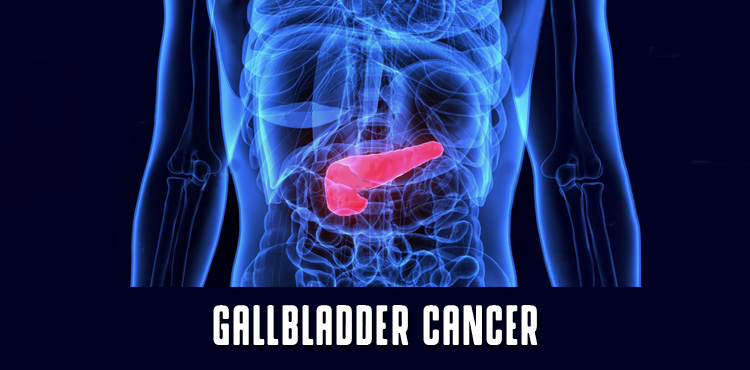
Gallbladder Cancer is a cancer that's found anywhere in the Gallbladder.
Your Gallbladder Cancer is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver.
Most Gallbladder Cancer begins in the glandular cells that line the inner surface of the gallbladder. Gallbladder Cancer that begins in this type of cell is called adenocarcinoma.
The Gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ under the liver. Both the liver and the gallbladder are behind the right lower ribs. In adults, the gallbladder is usually about 3 to 4 inches long and normally no wider than an inch.
Gallbladder Cancer Signs and Symptoms may include :
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right portion of the abdomen
- Abdominal Bloating
- Losing Weight without trying
- Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- Ichiness
- A Lump in your tummy
- Nausea and Vomiting
The following factors can Raise a person's Risk of developing Gallbladder Cancer :
- Smoking : Tobacco use may increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Inflammation of the bile ducts : Primary sclerosing cholangitis, which causes inflammation of the ducts that drain bile from the gallbladder and liver, increases the risk of gallbladder cancer.
- Family History : A family history of gallbladder cancer slightly increases a person’s risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
- Gender : Gallbladder cancer is found slightly more often in women than in men.
Tests and Procedures used to stage Gallbladder Cancer include :
- Blood Tests.
- Imaging Tests.
- Removing a sample of liver tissue for testing.
- Ultrasound
- Endoscopic or Laparoscopic ultrasound
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan
- Chest X-ray
Three Types of Standard Treatment are used :
- Surgery
- Radiation Therapy
- Chemotherapy