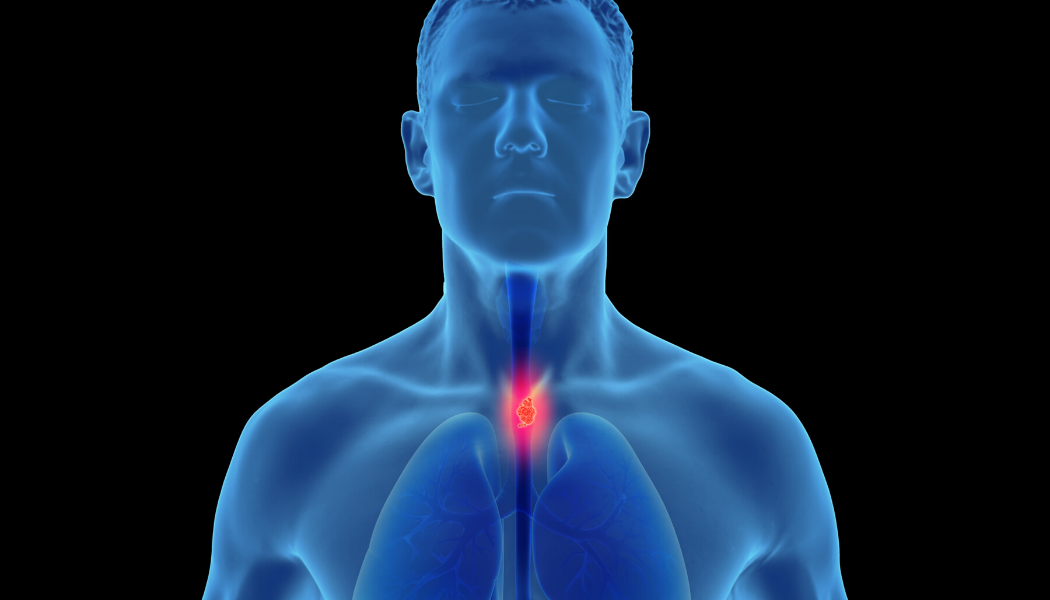
Esophageal Cancer is cancer that occurs in the esophagus a long, hollow tube that runs from your throat to your stomach. Your esophagus helps move the food you swallow from the back of your throat to your stomach to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer usually begins in the cells that line the inside of the esophagus. Esophageal cancer can occur anywhere along the esophagus. More men than women get esophageal cancer.
Esophageal Cancer commonly starts in the cells present in the internal lining of the esophagus.
Esophageal Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
The most Common Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer are :
- Hoarseness and Cough.
- Chest pain, Pressure or Burning
- A Lump under the Skin.
- Weight Loss.
- Painful or Difficult Swallowing.
- Bone Pain
- Men are at higher risk than women.
Risk Factors for Esophageal Cancer
- Being Overweight.
- Having Bile Reflux
- Having a steady habit of drinking very hot liquids
- Smoking.
- Not eating enough fruits and vegetables
- Drinking Alcohol
- Chewing Tobacco
Operations used to treat Esophageal Cancer include :
- Surgery to remove very small tumors :
If your cancer is very small, confined to the superficial layers of your esophagus and hasn't spread, your surgeon may recommend removing the cancer and margin of healthy tissue that surrounds it.
- Surgery to remove a portion of the esophagus (esophagectomy) :
During esophagectomy, the surgeon removes the portion of your esophagus that contains the cancer, along with a portion of the upper part of your stomach, and nearby lymph nodes. The remaining esophagus is reconnected to your stomach. Usually this is done by pulling the stomach up to meet the remaining esophagus.
- Surgery to remove part of your esophagus and the upper portion of your stomach (esophagogastrectomy) :
During esophagogastrectomy, the surgeon removes part of your esophagus, nearby lymph nodes and a larger part of your stomach. The remainder of your stomach is then pulled up and reattached to your esophagus. If necessary, part of your colon is used to help join the two.
As Esophageal Cancer advances, it can cause complications, such as :
- Obstruction of the Esophagus :
Cancer may make it difficult for food and liquid to pass through your esophagus.
- Pain :
Advanced esophageal cancer can cause pain.
- Bleeding in the Esophagus :
Esophageal cancer can cause bleeding. Though bleeding is usually gradual, it can be sudden and severe at times.